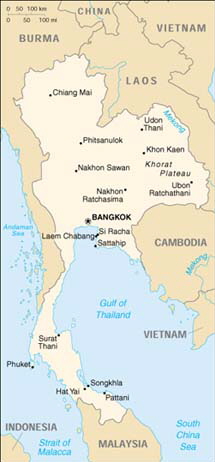
|
Population: 61,797,751 (July 2001 est. based on excess mortality due to AIDS)
Age structure: 23.43 % of the total population 14 years old or younger, 69.95% is 15 to 64 years old, and 6.62% is over 65 years of age. (2001 est.)
Population growth rate: 0.91% (2001 est.)
Birth rate: The average number of births for every 1000 people is 16.63 . (2001 est.)
Death rate: The average number of deaths for every 1000 people is 7.54. (2001 est.)
Net migration rate: There is virtually no change in population due to migration. The average change in population for every 1000 people is zero. (2001 est.)
Sex ratio: At birth, the ratio of boys to girls is 1.05:1. At age 65, the ratio of men to women is 0.78:1
Infant mortality rate: There are approximately 30.49 deaths for every 1,000 live births (2001 est.)
Life expectancy at birth: The average life expectancy of the total population is 68.86 years. For males it is 65.64 years & for females it is 72.24 years (2001 est.)
Total fertility rate: There is an average of 1.87 children born for every one woman in population (2001 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: approximately 2.15% of all adults have HIV/AIDS. The number of people estimated to be living with HIV/AIDS as of 1999 was 755,000 and the number estimated to have died with HIV/AIDS was 66,000 (Note: those numbers have since increased.)
Ethnic groups: 75% of all people in Thailand are considered to be Thai, 14% are Chinese, and all other groups together make up 11%.
Religions: 95% of all the people in Thailand are Buddhist , 3.8% are Muslim, 0.5% are Christian, 0.1% are Hindu, & all other religions make up 0.6% of the total. (based on 1991 statistics)
Languages: Thai is the primary language of the country with various ethnic and regional dialects. English is a secondary language spoken most fluently by the elite. There are also many languages spoken by various hilltribe groups.
Literacy: ( Literacy is defined as people who are age 15 or older and can read and write.) 93.8% of all the people in Thailand are literate. This includes 96% of the men and 91.6% of the women. (1995 est.)
Population below poverty line: 12.5% of all people in Thailand are considered to be living in poverty. (The definition of poverty was not given.) (1998 est.)
Jobs: Of all the people working in Thailand 54% work in agriculture, 15% work in industry, 31% work in services (1996 est.)
Budget: revenues: $19 billion expenditures, $21 billion, including capital expenditures (2000 est.)
Industries: tourism; textiles and garments, agricultural processing, beverages, tobacco, cement, light manufacturing, such as jewelry; electric appliances and components, computers and parts, integrated circuits, furniture, plastics; world's second-largest tungsten producer and third-largest tin producer
Electricity - production by source: fossil fuel: 91.17% hydro: 3.81% nuclear: 0% other: 5.02% (1999)
Agriculture - products: rice, cassava (tapioca), rubber, corn, sugarcane, coconuts, soybeans
Exports - commodities: computers and parts, textiles, integrated circuits, rice
Exports - partners: US 22%, Japan 14%, Singapore 9%, Hong Kong 5%, Netherlands 4%, Malaysia 4%, UK 4% (1999)
Imports - commodities: capital goods, intermediate goods and raw materials, consumer goods, fuels
Imports - partners: Japan 26%, US 14%, Singapore 6%, China 5%, Malaysia 5%, Taiwan 5% (1999)
Currency: baht
Exchange rates: history of baht per US dollar 2001 - 43.078=$1 U.S. dollar 2000 - 40.112=$1 1999 - 37.814=$1 1998 - 41.359=$1 1997 - 31.364=$1 1996 - 25.343=$1
Statistics source: CIA World Factbook
|